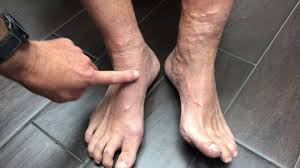
Lymphedema is a medical condition that causes swelling in an individual’s extremities (one or more). Impaired flow in the lymphatic system is the cause of the swelling.
Chronic venous insufficiency, also known as venous edema, is a serious disease of the veins that spreads to the lymphatic system. It usually worsens with time. The chronic leakage of the venous fluid into the tissues later compromises the lymphatic system.
Lymphedema And Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI)
CVI and lymphedema have similarities in that both diseases cause swelling of the feet and legs. However, the symptoms, causes and treatment can be different.
Many factors other than CVI can cause chronic edema of the lower extremities and, in some cases, contribute to lymphedema.
In CVI, chronic leakage of venous fluid into the tissues compromises the lymphatic function. Moreover, in CVI, leg veins do not allow blood to travel back to the heart, further resulting in the collection or pooling of the blood in the legs.
Though CVI can affect any part of the body, it mainly affects arms, hands, ankles, feet, and legs. These tissue changes make you vulnerable to wounds that are difficult to heal and may result in lymphedema.
However, lymphedema may also be caused as a result of infection, injury, or trauma of areas of the body or damaged lymph nodes from cancer treatment.
CVI patients experience changes in their lymphatic system. As the disease progresses, there is more likely to be swelling.
Difference Between CVI and Lymphedema
- Timing of onset: CVI mainly occurs in older people, mainly above 50 years of age. Lymphedema can occur at any age between childhood and middle-age.
- Pain: CVI-related pain mainly occurs during or after walking and is better by elevating the legs. Pain due to lymphedema may not be related to standing or walking. It is due to joint issues, swelling, or increased limb weight.
- Swelling: The swelling of CVI is mainly seen in the lower legs and ankles and is similar in both legs. CVI-related swelling is more during the day and reduces overnight during sleep. Lymphedema affects the entire leg, and the swelling is rarely symmetric. And this swelling does not subside at night.
- Treatment: Compression stocking aid in improving blood flow and help prevent pain and swelling due to CVI. Procedures to remove leaky veins may also be required. The primary treatment for lymphedema involves complex decongestive therapy.